
According to VSEPR, the valence electron pairs surrounding an atom mutually repel each other they adopt an arrangement that minimizes this repulsion, thus determining the molecular geometry. The valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) model predicts the shape of individual molecules based on the extent of electron-pair electrostatic repulsion. Using the 3d representation of atomic orbitals and the bonds they form leads to different angles between the bonds. The double bond between the two carbon atoms consists of a sigma bond and a π bond. The simplest example of an organic compound with a double bond is ethylene, or ethene, C 2H 4. The overlap does not occur between the nuclei of the atoms, and this is the key difference between sigma and pi bonds. Pi or π bonds occur when there is an overlap between unhybridized p orbitals of two adjacent atoms. Hybrid orbitals are denoted as sp x, where s and p denote the orbitals used for the mixing process, and the value of the superscript x ranges from 1-3, depending on how many p orbitals are required to explain the observed bonding.

The newly formed hybrid orbitals all have the same energy and have a specific geometrical arrangement in space that agrees with the observed bonding geometry in molecules. A combination of s and p orbitals results in the formation of hybrid orbitals. Hybridization describes the bonding situation from a specific atom’s point of view. They can occur between any kind of atomic orbitals the only requirement is that the atomic orbital overlap happens directly between the nuclei of atoms.ĭouble and triple bonds can be explained by orbital hybridization, or the ‘mixing’ of atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals.
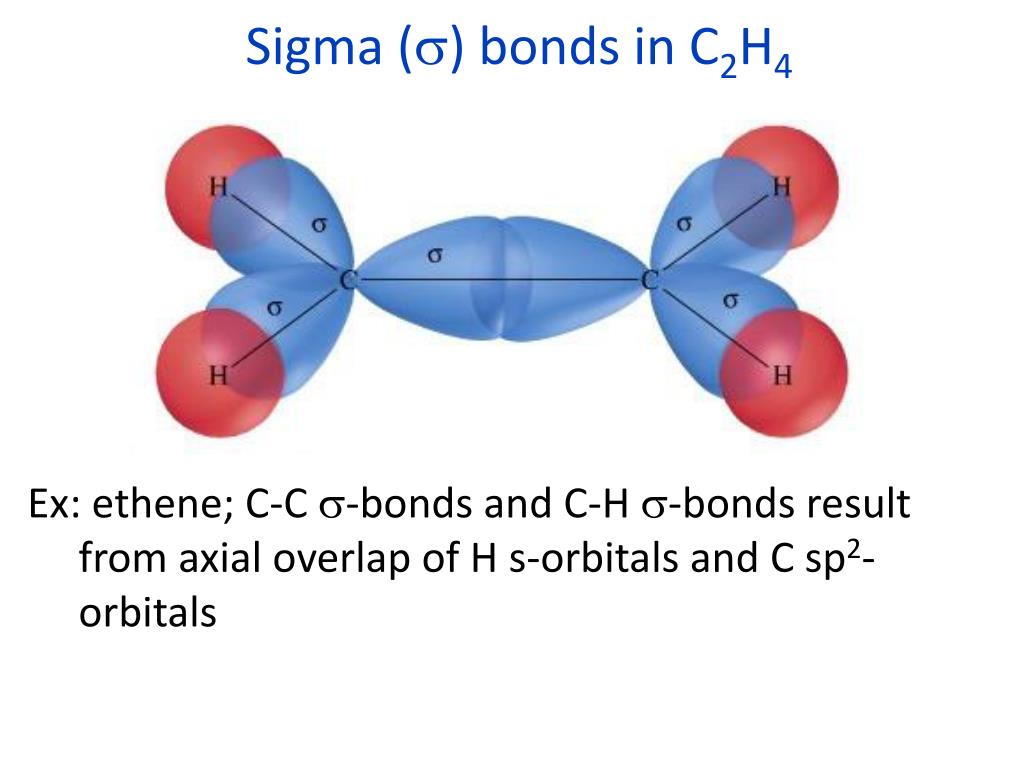
Sigma (σ) and Pi (π) bonds form in covalent substances when atomic orbitals overlap.Ī sigma bond σ is the strongest type of covalent bond in which the atomic orbitals directly overlap between the nuclei of two atoms.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
